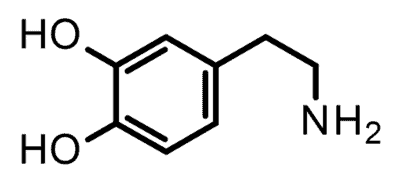
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is produced by neurons and acts to modulate the sensitivity of other neurotransmitters. It plays a major role in the brain’s reward system and in regulating pleasure and motivation. It is also involved in movement control, mood regulation, and cognition.
Dopamine plays a pivotal role in the formation and persistence of addiction. According to a study by Ingmar H.A. et al in 2005 ‘The role of dopamine in human addiction: From reward to motivated attention’ addictive substances or behaviors lead to an increase in dopamine levels in the brain.
This release creates feelings of pleasure and reinforces addictive behavior. Over time, the brain becomes desensitized to the effects of dopamine, leading individuals to seek out more of the substance or behavior to achieve the same level of pleasure. This cycle of seeking out and using addictive substances or engaging in addictive behaviors increases the chances of developing addiction, characterized by compulsive drug use or behavior despite deleterious consequences.
What is Dopamine?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, a brain chemical produced by neurons, critical for reward, motivation, movement, and mood. It reinforces pleasurable behaviors, regulates voluntary movement, and affects cognitive functions like attention and decision-making. According to Roy A. Wise and Chloe J. Jordan’s 2021 study ‘Dopamine, behavior, and addiction,’ all or almost all learned behaviors are dependent on dopamine function.
Dopamine’s release in response to rewarding stimuli motivates the repetition of those behaviors. An imbalance in dopamine levels impacts mood and is a major factor in disorders like Parkinson’s disease and addiction.
Is Dopamine a Pleasure Chemical?
Many people refer to dopamine as the pleasure chemical because of the central role it plays in the brain’s reward system. It is involved in the sensation of pleasure and reinforcement of behaviors associated with rewarding stimuli.
However, experts believe that although dopamine contributes to pleasure, it is not directly responsible for creating pleasurable feelings. It is involved in the sensation of pleasure and reinforcement of behaviors associated with rewarding stimuli. This is an important factor in the development and persistence of addiction.
What are The Functions of Dopamine?
As a neuromodulator, dopamine plays several important functions that go beyond the brain. Here is a list of functions:
Reward and Pleasure
Dopamine plays a central role in the brain’s reward system. It is released in response to pleasurable experiences such as eating tasty food or using certain drugs. This release of dopamine reinforces behaviors that are associated with pleasure, motivating individuals to repeat those behaviors.
Motivation and Reinforcement
Dopamine is involved in motivation and reinforcement processes. It helps regulate the initiation and persistence of goal-directed behavior. When dopamine level increases in response to a rewarding stimulus, it reinforces the behaviors that led to that reward, thereby causing a repeat of the behavior in the future.
Movement Control
Dopamine is also implicated in the control of movements, especially voluntary movement, where it plays a coordinating role. Dopamine also helps regulate motor skills. Research has shown that an imbalance in the dopamine system contributes to the development of movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease.
Cognition
Dopamine affects several cognitive functions such as working memory, attention, and executive function. Optimal dopamine levels are necessary for ensuring the smooth delivery of cognitive processes such as decision-making, problem-solving, and planning.
Mood Regulation
Dopamine is implicated in mood regulation, but this involvement is still being studied. The role of the neurotransmitter in mood disorders like bipolar disorder and depression is not fully understood. However, imbalances in dopamine levels have been associated with changes in mood and affective disorders.
Dopamine is more than the brain’s reward neuromodulator. It plays a crucial role in various aspects of brain function. Its intricate interplay with other neurotransmitter systems contributes to the complexity of brain function and behavior.
Its intricate interplay with other neurotransmitter systems contributes to the complexity of brain function and behavior.
How is Dopamine Produced and Secreted?
Dopamine is produced and secreted primarily in the brain, within specific regions referred to as dopaminergic pathways. The synthesis of dopamine begins with the amino acid tyrosine, which is mainly obtained from dietary sources. Tyrosine is converted to L-DOPA by an enzyme, tyrosine hydroxylase. This conversion takes place within neurons known as dopaminergic neurons.
L-DOPA is further converted into dopamine through the action of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase and stored in vesicles within dopaminergic neurons, awaiting release.
When a signal is received, dopamine is released from the vesicles into the synapse, the junction between neurons. Upon release, dopamine binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, initiating a series of biochemical reactions that transmit the signal onward.
Once dopamine has fulfilled its role, it is taken back up into the presynaptic neuron through a process called dopamine reuptake, mediated by dopamine transporters. Alternatively, it is broken down by enzymes known as monoamine oxidase and catechol-O-methyltransferase into inactive metabolites that are eliminated from the body.
The production and secretion of dopamine involves a series of biochemical processes that take place within the dopaminergic neurons, culminating in its release into the synapse to transmit signals between neurons in the brain.
Dopamine and Addiction: What is the Connection?
Dopamine plays a significant role in addiction due to its involvement in the brain’s reward system. When a person consumes substances or engages in activities that produce pleasure, dopamine levels in the brain increase. The surge in dopamine reinforces the behavior making it more likely for the individual to repeat it in the future.
Roy A. Wise and Chloe J. Jordan’s 2021 study ‘Dopamine, behavior, and addiction, further explains that the ability of certain substances to induce burst-like release of dopamine correlates with addiction. However, evidence for this correlation is seen more strongly in some substances like cocaine, amphetamine, and opiates, than in others.
Repeated exposure to said addictive substances or behavior causes a sort of desensitization to the effects of dopamine. Hence the brain demands higher levels of stimulation to experience the same pleasure. This phenomenon, known as tolerance, contributes to the escalation of addictive behavior.
However, while dopamine plays a role in the onset and persistence of addiction, it is not the sole perpetrator. A range of biological factors, like genes and health history, and environmental factors, such as social influences, all contribute to addiction.
What role does dopamine play in addiction?
Dopamine’s involvement in addiction stems from its role in the brain’s reward system. When a person engages in addictive behaviors or consumes substances, dopamine levels in the brain increase, reinforcing the behavior and motivating repetition.
How does dopamine dysregulation contribute to addiction?
Dysregulation of dopamine signaling results in the desensitization of dopamine receptors and the development of tolerance. Individuals may require higher levels of stimulation to experience the same pleasure, driving the escalation of addictive behavior. Long-term changes in the brain’s structure and function also occur, impacting decision-making, impulse control, and judgment.
Can dopamine-based treatments be effective in addiction management?
Research suggests that medications targeting dopamine receptors or the dopamine system may be useful in treating addiction. However, individual responses to these treatments vary, and they are often used in combination with behavioral therapies for comprehensive addiction management.
Can other neurotransmitter also cause Addiction?
Yes, let’s have a look at some:
How is Serotonin related to Addiction?
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that helps to regulate mood, behavior, and other vital body functions. It works in opposition to dopamine, another neurotransmitter involved in addiction.
Low levels of serotonin have been linked to impulsivity and addictive behaviors, as serotonin helps to regulate impulse control and decision making. Additionally, imbalanced levels of serotonin have been observed in individuals with substance use disorders and gambling addiction.
This further emphasizes the role of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, in the development and maintenance of addiction. To learn more about the link between serotonin and addiction, check out our article on it.
How is Adrenaline related to Addiction?
The relationship between adrenaline and addiction is complex. Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress or fear. In small amounts, it can have beneficial effects, such as increasing focus and alertness.
However, in excessive amounts and frequent release, it can contribute to addiction by producing a temporary feeling of euphoria and excitement, which can reinforce addictive behaviors. Moreover, chronic stress and high levels of adrenaline can lead to a dysregulation of the dopamine system, making individuals more vulnerable to addiction.
This is because dopamine is also involved in the brain’s response to stress and can be triggered by adrenaline, contributing to the reward and reinforcement cycle of addiction.
To learn more about the interaction between adrenaline and addiction, read our article on the Role of Stress in Addiction.
Get help for your Addiction
Addiction Treatment at Olympic Behavioral Health offers help and support for those struggling with addiction. Taking the first step can be difficult, but it is crucial to call for assistance. Our facility in West Palm Beach provides comprehensive addiction treatment programs to guide individuals towards recovery. If you or your loved one is battling addiction, reach out to Olympic Behavioral Health today.

Share This Post



